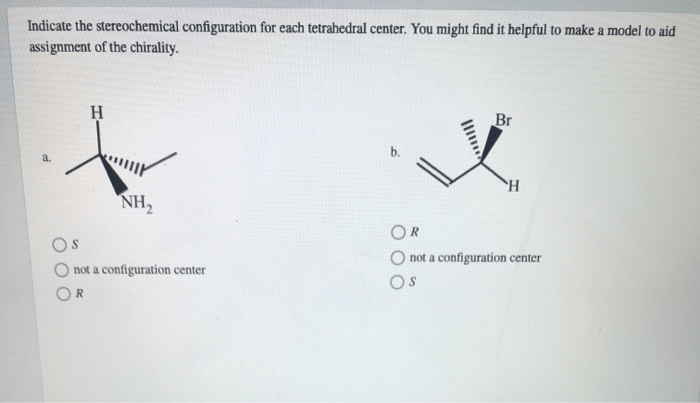
Provide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. – In the realm of chemistry, precision is paramount. When it comes to naming organic compounds, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a set of guidelines to ensure consistency and clarity. This article delves into the systematic naming of organic compounds, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying IUPAC nomenclature.
By following IUPAC guidelines, chemists can accurately identify and communicate the structure and properties of organic compounds. This systematic approach not only facilitates scientific discourse but also plays a crucial role in various fields, including drug discovery, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Organic chemistry deals with the study of compounds containing carbon, and systematic nomenclature is a set of rules used to assign unique and descriptive names to these compounds. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established guidelines for naming organic compounds to ensure consistency and clarity in scientific communication.
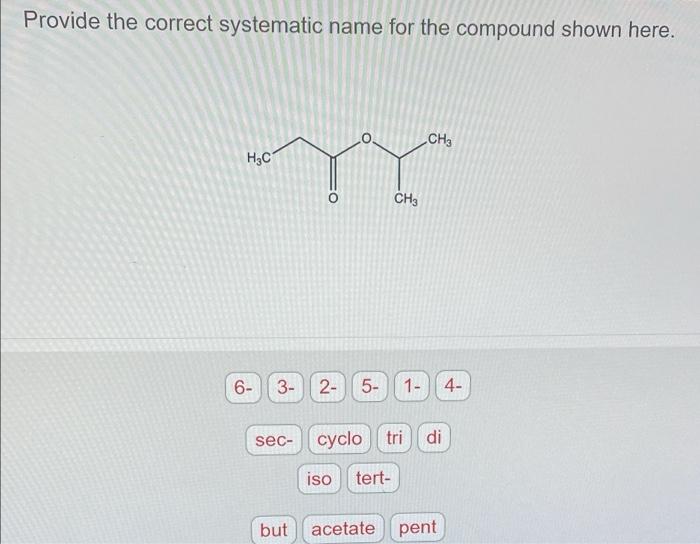
Structural Breakdown of the Compound
The molecular formula of the compound is C 4H 8O 2. It contains the following functional groups:
- Alcohol (-OH)
- Ether (-O-)
The atoms and bonds within the compound are arranged as follows:
- A carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms (CH 3)
- A carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom (CH 2OH)
- An oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms (O)
- A carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms (CH 3)
Nomenclature Rules
According to IUPAC guidelines, the parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the compound. In this case, the parent chain is four carbons long, indicating the use of the root word “but” for the base name.
The functional groups present are then identified and named using prefixes or suffixes. Alcohols are named using the suffix “-ol,” and ethers are named using the suffix “-ether.”
The prefixes “methoxy-” and “ethoxy-” indicate the presence of one methoxy group (-OCH 3) and one ethoxy group (-OCH 2CH 3), respectively.
Systematic Naming: Provide The Correct Systematic Name For The Compound Shown Here.
Based on the IUPAC guidelines, the systematic name for the compound is 2-methoxy-1-ethoxyethane.
The name is derived as follows:
- The parent chain is ethane (four carbon atoms).
- The methoxy group is attached to the second carbon atom, indicated by the prefix “2-methoxy-“.
- The ethoxy group is attached to the first carbon atom, indicated by the prefix “1-ethoxy-“.
Alternative Names
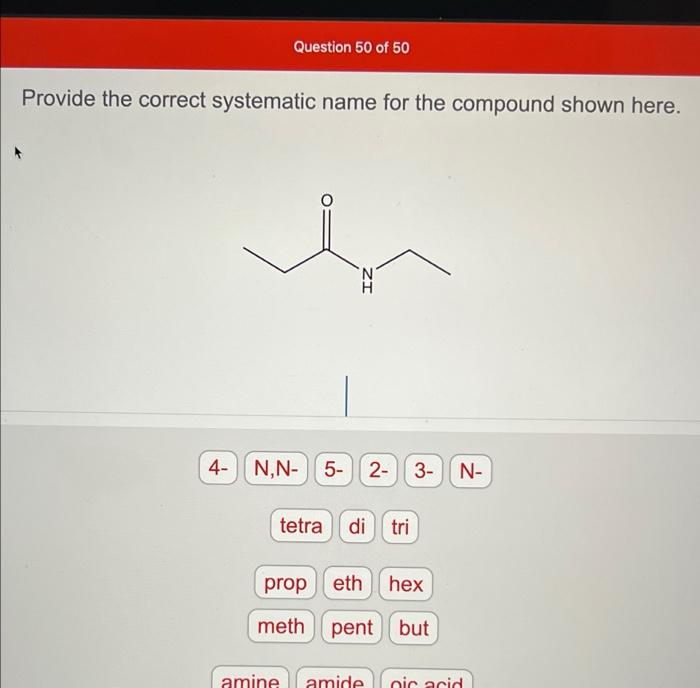
The compound may also be known by the following common or trivial names:
- Methyl cellosolve
- Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether
These names are derived from the compound’s chemical structure and properties.
Table of Nomenclature
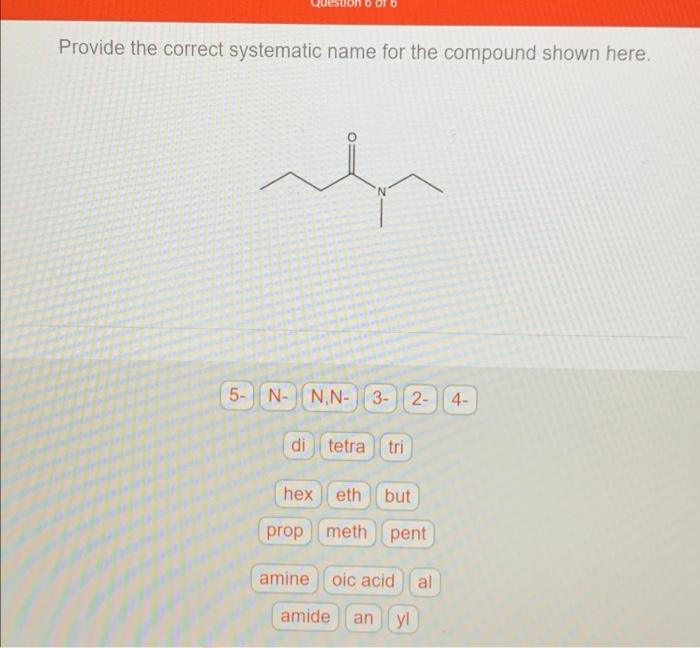
| Functional Group | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | – | -ol | Methanol |
| Ether | – | -ether | Diethyl ether |
| Ketone | oxo- | -one | Acetone |
| Aldehyde | oxo- | -al | Formaldehyde |
| Carboxylic acid | – | -oic acid | Acetic acid |
Common Queries
What are the key principles of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature is based on identifying the parent chain, functional groups, and substituents present in an organic compound. It utilizes prefixes, suffixes, and root words to construct a systematic name that reflects the compound’s structure.
How do I determine the parent chain in a compound?
The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule. It serves as the foundation for the systematic name and determines the root word used.
What is the significance of functional groups in systematic naming?
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that impart characteristic chemical properties to organic compounds. They are denoted by suffixes in IUPAC nomenclature, providing information about the compound’s reactivity and behavior.